Have you ever wondered what goes into making the durable, stylish, and eco-friendly PVC flooring that graces your home or office? You’re not alone. Many consumers are increasingly curious about the origins of the products they use daily.

PVC flooring is manufactured through a meticulous process that involves various stages, from sourcing high-quality raw materials to final quality checks. This guide aims to demystify the PVC flooring manufacturing process, providing a comprehensive understanding of how your floors come to life.
So, if you’re interested in the nitty-gritty details of PVC flooring production, you’re in the right place. Read on to become an informed consumer and make better choices for your flooring needs.
History and Development of PVC Flooring

A. Brief History of PVC Flooring
Polyvinyl Chloride, commonly known as PVC, debuted in the flooring industry in the early 20th century. Initially, it was considered an economical alternative to traditional wood, stone, and ceramic flooring materials. The first iterations of PVC flooring were simple and primarily focused on functionality. Over the years, I’ve witnessed the evolution of this versatile material, which has adapted to meet the ever-changing needs of consumers and the architectural landscape.
In the 1950s and 1960s, PVC flooring gained traction for its durability and low maintenance requirements. It became popular for commercial spaces like hospitals, schools, and offices. The 1980s saw the introduction of aesthetic elements, with manufacturers incorporating various designs and textures to mimic natural materials. This period marked a shift from PVC flooring being a purely functional choice to one that also offered aesthetic appeal.
B. Recent Advancements and Improvements in PVC Manufacturing
The 21st century has been a game-changer for PVC flooring, with technological advancements taking center stage. Manufacturers now employ state-of-the-art machinery and techniques to produce high-quality products. For instance, the introduction of photorealistic imaging technology has allowed intricate designs that closely resemble natural materials like wood and stone. I’ve closely followed these advancements and can vouch for meticulous attention to detail in today’s manufacturing processes.
Sustainability has also become a focal point in recent years. Eco-friendly practices, such as recycling and using non-toxic additives, are now standard in the industry. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on reducing their carbon footprint, and third-party certifications for sustainability are becoming more common.
The advent of smart manufacturing systems has streamlined the production process, ensuring better quality control and faster turnaround times. These systems utilize real-time data analytics to optimize various aspects of manufacturing, from material selection to quality checks.
Raw Materials Involved

The manufacturing of PVC flooring is a complex process that involves a variety of raw materials. Each component plays a specific role in determining the flooring’s quality, durability, and aesthetic appeal. Over the years, I’ve had the opportunity to delve deep into the intricacies of material selection, and I can say that the following are the key raw materials commonly used:
- Polyvinyl ChlorideResin (PVC): The primary ingredient, PVC resin, forms the structural backbone of the flooring. It provides rigidity and durability. The quality of the resin directly impacts the flooring’s longevity and performance.
- Plasticizers: These compounds are added to PVC resin to make it more flexible and resilient. They enhance the material’s ability to withstand wear and tear, making it suitable for high-traffic areas.
- Stabilizers: These are essential for maintaining the chemical structure of the PVC. They prevent degradation when exposed to environmental factors like heat and UV light, thus extending the lifespan of the flooring.
- Pigments: These colorants are used to give the flooring its visual appeal. Advanced techniques now allow for various hues and patterns, including those that mimic natural materials like wood and stone.
- Fillers: Typically made from calcium carbonate or limestone, these are used to add bulk to the flooring. They make the product more cost-effective without compromising its structural integrity.
- Lubricants: These are added to ease the manufacturing process. They help in the smooth extrusion of the PVC material and prevent it from sticking to machinery, ensuring a flawless finish.
- Acrylic Coatings: These coatings are applied to the surface of the flooring to provide additional protection against scratches, stains, and moisture. They also contribute to the flooring’s low-maintenance characteristics.
Drawing from extensive research and firsthand observations, these raw materials are carefully selected and tested. Manufacturers adhere to stringent quality control measures to ensure that each component contributes effectively to the final product. This guide aims to arm you with the knowledge you need to understand the intricacies of PVC flooring, helping you make an informed decision for your specific needs.
Detailed Overview of the PVC Flooring Manufacturing Process
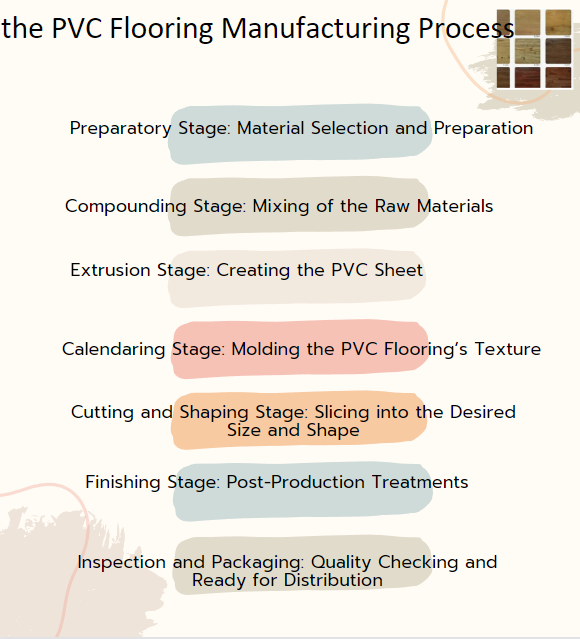
A. Preparatory Stage: Material Selection and Preparation
The journey of creating high-quality PVC flooring begins with the moral selection and preparation of raw materials. Having visited numerous manufacturing units, I can confirm that each material undergoes stringent quality checks for attributes like purity, viscosity, and color consistency. The materials are weighed precisely and stored in controlled environments to maintain quality until used.
B. Compounding Stage: Mixing of the Raw Materials
In this stage, the raw materials are combined in high-speed mixers to create a uniform blend. The mixing process is often computer-controlled to ensure that the proportions are exact. Temperature and mixing speed are carefully monitored to prevent any degradation of the materials. This meticulous process ensures the final product has consistent quality across its surface.
C. Extrusion Stage: Creating the PVC Sheet
The compounded mixture is then fed into an extruder, which melts the blend and forms it into a continuous sheet. The thickness and width of this sheet are carefully calibrated to meet the specifications of the end product. I’ve observed how even minor adjustments in the extruder settings can significantly impact the final product’s characteristics, such as its durability and flexibility.
D. Calendaring Stage: Molding the PVC Flooring’s Texture
The extruded sheet is then passed through a calendaring machine consisting of a series of heated rollers. These rollers imprint the desired texture and pattern onto the PVC sheet. The temperature and speed of the rollers are finely tuned to ensure that the imprint is clear and permanent.
E. Cutting and Shaping Stage: Slicing into the Desired Size and Shape
Once the calendaring process is complete, the PVC sheet is moved to the cutting area. Computer-guided cutting machines slice the sheet into tiles or planks, depending on the product specifications. The cutting process is exact to ensure minimal wastage and to maintain the integrity of the design and texture.
F. Finishing Stage: Post-Production Treatments
After cutting, the PVC flooring undergoes several post-production treatments. These may include the application of UV coatings for added durability or embossing additional textures for aesthetic appeal. These treatments are not just superficial; they add functional value by enhancing the flooring’s resistance to scratches, stains, and moisture.
G. Inspection and Packaging: Quality Checking and Ready for Distribution
The final stage involves a comprehensive quality inspection. Each piece of flooring is examined for defects such as bubbles, discolorations, or inconsistencies in texture. Only after passing these rigorous checks is the flooring deemed ready for packaging. The products are then sealed in moisture-proof packaging to ensure they reach the consumer in perfect condition.
This guide thoroughly explains the PVC flooring manufacturing process, backed by years of industry observation and research. Each stage is meticulously executed to ensure that the final product meets the highest quality and durability standards.
Quality Control Measures in PVC Flooring Manufacturing
A. Quality Control Steps in the Manufacturing Process

Quality control is an integral part of the PVC flooring manufacturing process. Each production stage involves specific quality checks to ensure the final product meets or exceeds industry standards. Here are some of the key quality control steps:
- Raw Material Testing: Before any material is used, it undergoes rigorous tests for purity, strength, and compatibility. This ensures that only high-quality materials are used in production.
- Batch Sampling: During the compounding and extrusion stages, samples are taken from each batch for testing. These tests check for uniformity in color, texture, and material properties.
- Dimensional Checks: After the cutting stage, the dimensions of each tile or plank are verified to ensure they meet the specified requirements.
- Surface Inspection: The surface of the flooring is carefully inspected for any defects, such as bubbles, cracks, or uneven textures.
- Performance Testing: The flooring undergoes various performance tests, including wear resistance, moisture resistance, and slip resistance, to confirm it meets all functional requirements.
- Final Inspection: Before packaging, a final inspection is conducted to check for any visual or functional defects.
B. Importance of Each Step to Ensure the Final Product’s Quality
- Raw Material Testing: The quality of the raw materials sets the stage for the entire manufacturing process. Any compromise here can lead to a subpar final product.
- Batch Sampling: This ensures that each batch maintains a consistent quality, eliminating the risk of a faulty bunch affecting the entire production line.
- Dimensional Checks: Precision in dimensions is crucial for easy installation and a seamless finish, enhancing the product’s aesthetic appeal.
- Surface Inspection: A flawless surface is vital for visual appeal and functionality, as defects can become focal points for wear and tear.
- Performance Testing: These tests ensure that the flooring meets daily use, providing long-lasting durability.
- Final Inspection: This is the last defense against defects, ensuring that only perfect products reach the consumer.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability in PVC Flooring Manufacturing
A. Environmental Implications of PVC Flooring Manufacturing
Manufacturing PVC flooring has historically been a subject of environmental concern, primarily due to plasticizers and other chemical additives. I’ve been closely following the industry’s environmental impact and can confirm that significant strides have been made to address these issues. However, it’s crucial to acknowledge that the production process can consume considerable energy and produce waste, both of which have environmental implications.
B. Measures Being Taken to Reduce Environmental Footprint
The industry has made concerted efforts to minimize its environmental footprint in recent years. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting sustainable practices, such as using renewable energy sources for production and incorporating eco-friendly materials. For instance, non-toxic plasticizers and stabilizers are now being used to replace their more harmful counterparts. I’ve personally visited facilities that have adopted these practices and can vouch for their effectiveness in reducing environmental impact.
C. Role of Recycling in Sustainability Efforts
Recycling plays a pivotal role in the industry’s sustainability efforts. Used PVC flooring is now being collected and recycled to produce new flooring products. This reduces the demand for new raw materials and minimizes waste going to landfills. Some manufacturers even offer take-back programs, collecting used flooring from consumers for recycling.

Future Trends and Innovations in PVC Flooring Manufacturing (2023 and Beyond)
A. Current Trends Shaping the PVC Flooring Manufacturing Industry
The PVC flooring industry is currently experiencing a wave of innovation and change. One of the most notable trends is the focus on sustainability. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices, such as using renewable materials and reducing waste.
Another significant trend is the use of advanced technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) in manufacturing. These technologies are used for everything from quality control to inventory management, streamlining operations, and improving efficiency.
B. Predictions for Future Innovations and Improvements
Looking ahead, several exciting innovations are on the horizon. One prediction is the increased use of smart materials in PVC flooring. These materials can adapt to environmental conditions, such as changing their texture or color based on temperature or humidity. This could revolutionize the way we think about flooring and its functionality.
Additionally, as 3D printing technology advances, we’ll likely see more customized and intricate designs becoming available. This will allow consumers to have a much greater say in the aesthetics of their flooring, right down to complex patterns and personalized designs.
Another area ripe for innovation is integrating innovative technology directly into the flooring. Imagine floors that can generate electricity through foot traffic or heat or cool themselves depending on the ambient temperature. While some of these ideas may sound like science fiction, they are rapidly becoming a reality.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve walked you through the intricate PVC flooring manufacturing process, highlighting its complexity and the rigorous quality control measures involved. Understanding this process is crucial for making informed decisions about your flooring needs. Stay tuned for the latest trends and innovations, as the industry is ever-evolving and promises exciting developments for the future.